COVID-19 Antibody vs. PCR Testing; When to Relax Social Distancing?
Welcome to another MedCram COVID-19 update. We are headed close to two million total confirmed and a hundred and fourteen thousand total deaths. And Turkey actually is moving up in terms of new cases. The United States and the UK are both also at the top in terms of new deaths.
When it comes to the University of Washington model, we can see here that we may be at the peak or coming very close to it here in the United States. It also seems as though in New York, we’re getting close to the peak as well and hopefully we’ll start to see some decline very shortly. Of course New York is a bit ahead of California. I think California is going to see some worsening here at least over the next week. It looks as though by April 15. We should start to see a decline in the deaths as well.
I want to talk a little bit about testing because that’s going to be something that’s going to be in the news here for the next couple of weeks. So I want to make sure you understand what’s going on in terms of testing. Now up to this point, the testing that’s been going on has been something called reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. I want you to understand what that is.
So the sample is obtained from your nose. Basically a nasopharyngeal swab is put up there and they get some of the mucus and they put it in a test tube for testing
. What we’re actually looking at here is the RNA. So here we have a strand of viral RNA and it’s single-stranded. So the base pairs are exposed and those base pairs are in a very specific order. What we do at this point is we add nucleotides in that will bind to these in a complementary pattern and will form a DNA strand and we use something called reverse
transcriptase because we’ve got to go from the RNA to the DNA. Great. Now we have a DNA. And then what we do is we basically go through a cycle where these things will unpair and then we’ll use an enzyme to copy that one.
And then we’ll tear them apart by heating them up or by using some other means.
And then we’ll do the process all over again. And you can see so for and so forth. And so basically what you’re doing is you’re taking one strand of viral RNA and you’re going to start to make a whole bunch of strands that are the same as and complementary to that original strand. And then what you’ll do is you’ll be able to detect a specific pattern by putting a probe down.
And if it’s in a specific order, you’ll be able to detect it somehow with a probe that matches up particularly with that sequence and you’ll get a positive result.
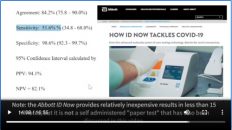
You can see that there’s a lot of steps involved in this process. And if anything goes wrong at any point along this process, you’re going to get a negative result, even though the virus is actually there. This is called a false negative result and sometimes it’s not that bad. Some
times you don’t get a lot of false negatives. But as the false negatives go up, the sensitivity of the test goes down. So you want to increase the sensitivity in this case because that’s going to reduce your false negatives. And in this case, it’s very important not to have false negatives because you might have a patient who is positive for COVID-19 that you’re going to treat as if they were negative. But the thing that I want you understand is the reverse transcriptase PCR is looking for actual evidence of the virus inside your
body. And so if we find the virus either in your nasal secretions or in the stool or in any sort of samples, that means the virus is still there.
Now that’s completely different than what we’re about to talk about which is antibody testing. So you have these cells called monocytes macrophages which eat foreign particles and present it to the adaptive immune system.
And they detect cells that have been infected with the virus. So here’s a cell that’s been infected with the virus and a macrophage will come along with a nice big nucleus and it will basically engulf it, kill the cell. And now what happens is this macrophage which is now eating part of the cell or all of it, perhaps, will chomp up and put on its receptors out here, parts of the
cell, and then you will have a T cell come along and we’re trying to be as generic as we can. It will present the antigen to the T cell and then the T cell will cause memory to remember this. It will also stimulate B cells to make antibodies, plasma cells, generally speaking, are the ones that make antibodies. And it turns out that these antibodies will specifically bind to these antigens and destroy.
And so what does this mean? If we start to see antibodies then that means the body has built in adaptive immunity. And you can actually test for these antibodies. So if you have a positive antibody test here on this side, this does not mean that you have the virus necessarily. It’s possible to have the virus. But what it does mean is that you have been infected in the past, number one. And now you have immunity because you have antibodies. The only way you could have
anti
bodies built up against this virus is if you had this first part here known as the innate immune system, which finds these viral particles and presents them to the T cells then the T cells stimulate the B cells and plasma cells to make antibodies. So why is this important? Because if you have antibodies, then that generally speaking means that you can’t be reinfected again. Now that is a probable statement. It is possible that if the virus mutates
enough and is able to get in you won’t have an immune response against it because if this antibody is against a particular part of this virus that mutates, now the virus can go and get into your body and not be attacked by the antibodies.
Now, we’ve talked before about this in MedCram update 42. So if you go back to update 42, you’ll hear us talking about the study with the monkeys and what they did with the monkeys was they infected
them and then once antibodies were made and the tests were negative. They try to reinfect them with the same virus and they were unable to. So that is a reassuring study but we still don’t know how long those antibodies last and if the virus mutates whether you could be reinfected again. This is what happens with the cold. This is what happens with influenza, right? Influenza mutates every year and that’s why you need a shot every year for the new version of
the flu virus.
So that may be what’s going to happen with coronavirus, we don’t know yet. It seems as though the experts believe that the coronavirus will come back on a yearly basis at least for the next couple of years, hard to say.
While there are planning on doing a number of large-scale COVID-19 antibody testing in the Southern California area and the they’re gon’ probably be doing it a lot in your area because this may be the key to getting people back to work because if people have the antibodies, these are the people that could probably go back to work and not have to worry a lot about reinfection or spreading it. And the reason why this is important as we believe that we’re missing a lot of coronavirus positive cases and if we’re able
figure out how many people in the population might already have been exposed to this. Then we can know better about when to end this social distancing and this isolation.
So let me give you a little bit of a rundown on antibody testing currently. It’s kind of what they call the wild wild west and that’s because the FDA has relaxed its restrictions on what companies can make. So the first thing that you ought to know is there’s a lot of scams that make
you think that you’re getting an FDA-approved test, but you’re not really getting an FDA approved or even a test that’s even worthwhile doing. There are no FDA-approved home kit. So if anyone tells you that you can buy a home kit and this is going to tell you whether or not you’ve got antibodies. It’s a scam. This is on April 12, 2020, there maybe in the future. Now in terms of lab based, in other words, all of the antibody tests have to be run in a specific lab of some sort and one lab
based company that has been FDA-approved is in North Carolina called Cellex, but there are 70 other companies that according to this article have legitimate tests and they have to give you that kind of a documentation but these have not been FDA-approved because they’re trying to get these tests up and running as quickly as possible. And there’s a number of news articles that are describing this and we will give you a link in the description below.
So how is antibody testing gonna tell us
about the population. Well, what you first have to do is define your population. And if this is your population here, what you want to do is take a random sampling of that population and figure out what percent of that population is positive and then you can make extrapolations to your actual population in total. And that’s the key though is defining what population that is. So you want to make sure it’s a random sampling.
I remember when I was in
college at the University of California Riverside. We had a population biology class. And one of the things that we did was we went up into the hills and we collected, this is very memorable for me, we collected 100 pill bugs, a hundred of them, and we have to take liquid paper with us and we had to paint a specific color of liquid paper on the backs of these poor little roly-polies or pill bugs as we call them. And that was what we did the first week. And then we release
’em all back onto the ground and let them go. And what we were figuring is that they were going into their population, whatever their population was. And then what we did was, a week later, we came back and we collected another box of a hundred pill bugs. Of course, it wasn’t the same hundred pill bugs because those first hundred pill bugs went back into the population and they mixed around at random. Do you know how many were colored with the same
color of Liquid Paper? There were two. Two pill bugs that were the same color. So what we were able to do was make an abstraction based on first that the hundred pill bugs that we collected represented just 1/50, right? Because we had two out of the whole hundred of the actual population. And so we were able to figure out what the total population was of those pill bugs based on doing this experiment. That’s not exactly what
we’re doing here, but it kind of tells you how to define the population. It’s important if you define the population because when you take a sampling of that population, it’s going to have to be homogeneous enough for you to make an assumption that if 5% of this small portion of the population is infected that in fact, 5% of the larger population is infected. Or in this case, since we’re looking for antibodies if 5% have antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, then 5% in the entire
population would. My lab partner who helped me with this was my girlfriend and is now my wife. So we always reminisce about the pill bugs.
A couple other points to talk about in terms of antibody testing. If you’re a healthcare provider and you have a positive antibody and if they are immune to it, then they wouldn’t have to wear PPE above and beyond what they would normally have to wear. If you’re a teacher for instance, you don’t have to worry about going back to school and getting infected. You’re not going to be able to pass it off to anybody. The other thing that’s important to know is if we’ve really underestimated the number of infections out there and it’s already up to 20, 30, 40,
50 percent, we could already be heading into the herd effect or the herd immunity effect. The herd effect is that if you have a person that is positively infected, that virus only has a certain period of time before it’s going to disappear in that person, either because the body takes care of the virus or because unfortunately the virus takes care of the body. Either way, the only way that virus can live on with progeny is to get into another human body. And at the beginning,
it’s really easy because all of the bodies around it that it could jump into are going to be negative. It’s never seen that virus before and so it’s really easy to make that jump. However, if you have a situation where a lot of the people around you have already been infected and have antibodies, it’s going to be harder for that virus to find a person that it can jump to and infect. And if infect, it can’t do it, it eventually dies and now the virus doesn’t spread anymore. It’s are not
starts to go less than 1 and when that happens the virus has only a matter of time before becomes extinct. And this is one thing that I would love to put on the endangered species list is COVID-19. So look for the discussion the next couple of weeks to shift from the number of people that are positive and the number of deaths in the hospital because those will start to come down, we believe here in the next week or two. And the discussion will start to
shift to what do we need to do to get back to work? What kind of antibody tests that we need to have? What documentation do we need to have? I think that’s going to be a very interesting discussion.
So a lot of you have commented and asked for some practical approaches to exactly what does hydrotherapy entail or hydrothermal therapy. And this website is the result of a lot of work put in by a physiotherapist or physical therapist in Australia who’s had a number of years of experience
setting up hydrotherapy sites throughout Asia and also painstakingly researching the approaches and the techniques that were used a hundred years ago during the 1919 flu pandemic.
So as many of you know, there’s opportunities to volunteer your services in New York. the National Health Service in the UK reached out to us and wanted us to make you aware that they are also looking for help there in the UK. And they are looking for registered and unregistered
health care workers as well, as a range of key roles in non-clinical areas. I have a special connection to the United Kingdom. My mother trained in nursing at the Queen Elizabeth School of Nursing in Birmingham back in the 1960s. And of course she’s retired now. But if there’s anyone that can help in this situation, please go to this website. We’ll put a link in the description below. We’ll see you next time.




Add comment